/etc/rsyncd.conf¶
In the previous article rsync demo 02 we introduced some basic parameters. This article is to supplement other parameters.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| fake super = yes | yes means that you do not need the daemon to run as root to store the complete attributes of the file. |
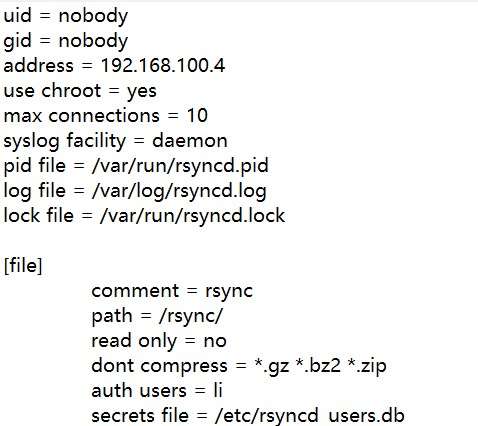
| uid = | user id |
| gid = | Two parameters are used to specify the user and group used to transfer files when running the rsync daemon as root. The default is nobody |
| use chroot = yes | Whether the root directory needs to be locked before transmission, yes yes, no no. In order to increase security, rsync defaults to yes. |
| max connections = 4 | The maximum number of connections allowed, the default value is 0, which means that there is no restriction |
| lock file = /var/run/rsyncd.lock | The specified lock file, which is associated with the "max connections" parameter |
| exclude = lost+found/ | Exclude directories that do not need to be transferred |
| transfer logging = yes | Whether to enable ftp-like log format to record rsync uploads and downloads |
| timeout = 900 | Specify the timeout period. If no data is transmitted within the specified time, rsync will exit directly. The unit is seconds, the default value is 0 means never time out |
| ignore nonreadable = yes | Whether to ignore files to which the user does not have access rights |
| motd file = /etc/rsyncd/rsyncd.motd | Used to specify the path of the message file. By default, there is no motd file. This message is the welcome message displayed when the user logs in. |
| hosts allow = 10.1.1.1/24 | Used to specify which IP or network segment clients are allowed to access. You can fill in the ip, network segment, host name, host under the domain, and separate multiples with spaces. Allow everyone to access by default |
| hosts deny = 10.1.1.20 | Which ip or network segment clients specified by the user are not allowed to access. If hosts allow and hosts deny have the same matching result, the client cannot access eventually. If the client's address is neither in the hosts allow nor in the hosts deny, the client is allowed to access. By default, there is no such parameter |
| auth users = li | Enable virtual users, multiple users are separated by commas in English state |
| syslog facility = daemon | Define the level of system log. These values can be filled in: auth, authpriv, cron, daemon, ftp, kern, lpr, mail, news, security, syslog, user, uucp, local0, local1, local2 local3, local4, local5, local6 and local7. The default value is daemon |
Recommended configuration¶
Author: tianci li